Best Sunscreens for Dark Skin Tones Without White Cast
Our favorite sunscreens for medium to darker skin tones
Best overall by the metrics
La Roche Posay Anthelios UV Correct Sunscreen Moisturizer SPF 70
Why it’s great: Moisturizing, no white cast, applies easily, broad spectrum SPF 70 protection.
Drawbacks: Minimal scent likely from components of the product
Type of protection: Chemical (glossary)
Price per unit at time of testing: $17.64 per oz, but value-packed and we say worth it
SkinSafe rating: A (‘A’ = top allergen free, according to skinsafeproducts.com)
What our testers (blinded) had to say about it:
“I want to know what this one is!”
“Reminds me of a day by the pool”
“Looks great on brown skin - I would wear this”
Best splurge-worthy purchase
UNSEEN SUNSCREEN Supergoop SPF 40
Why it’s great: Easy to rub in, no white cast (glossary), broad spectrum SPF 40 protection, and minimal scent.
Drawbacks: Slightly greasy texture, small bottle size
Type of protection: Chemical
Price per unit at time of testing: $20 per oz, like we said … splurge-worthy
What our testers (blinded) had to say about it:
“This would go well under my makeup or as a primer”
“This feels expensive and luxurious”
“I would purchase stock in this” (Note to our readers: please alert Dr. Nelson Ugwu should Supergoop become publicly traded on the NYSE 🤣🤣🤣)
Best budget pick
Neutrogena Beach Defense SPF 70
Why it’s great: Affordable, minimal white cast, broad spectrum SPF 70 protection, and easy to rub in. Smells like childhood nostalgia
Drawbacks: May not be for users who are sensitive to scented products
Type of protection: Chemical
Price per unit at time of testing: $1.34 per oz, the most cost-effective product we tested
What our testers (blinded) had to say about it:
“Has a floral scent, it’s not bad”
“Gives a shiny quality to my skin”
“It reminds me of a day at the beach”🌞🏖️🏝️
Best tinted sunscreen
TIZO Facial Primer Tinted Mineral Sunscreen SPF 40
Why it’s great: Applies and blends easily on medium to darker skin tones. Contains iron oxide to protect against hyperpigmentation from visible light (glossary)
Drawbacks: May not be ideal for lighter skin tones
Type of protection: Mineral (glossary)
Price per unit at time of testing: $24.57 per oz
SkinSafe rating: A+ (deemed the highest tier of hypoallergenic skincare products)
What our testers (blinded) had to say about it:
“Has yellow to light brown undertones. Great for medium to brown skin”
“Provides a mattifying silicone finish”
“Would go well with makeup”
Best for users with a dry skin profile
Neutrogena Hydro Boost Hyaluronic Acid Facial Moisturizer with Broad Spectrum SPF 50
Why it’s great: Hydrating, easy to rub into the skin, minimal white cast, soothing texture, broad spectrum SPF 50
Drawbacks: Slight odor, but likely from components of product and not added fragrance
Type of protection: Chemical
Price per unit at time of testing: $9.98 per oz, well-priced for the quality
What our testers (blinded) had to say about it:
“Light and shiny, yet hydrating”
“I would buy this!”
“This would be good for people with dry skin profile”
Best for users with a oily or combination skin profile
Innisfree Daily UV Defense Sunscreen Broad Spectrum SPF 36
Why it’s great: Easy to apply, no white cast, broad spectrum SPF 36 protection
Drawbacks: Stronger odor among the products we tested
Type of protection: Chemical
Price per unit at time of testing: $8.82 per oz
What our testers (blinded) had to say about it:
“This would go well on oily skin profiles”
“This is my second favorite pick!” - Dr. Nelson Ugwu
“Smells like Skittles!”🌈🍬
-
In our extensive experiment, we set out to evaluate and compare 22 different sunscreens and determine which are more compatible with a diverse range of medium to darker skin tones. Our testing team, consisting of dermatology residents with diverse skin types, tones, and ethnicities, rigorously examined each product's performance.
We assessed criteria including:
Presence or absence of white cast
Ease of application
Greasiness
Odor and allergenicity
Any immediate side effects on the skin
Overall user experience
We assumed that the SPF level associated with each sunscreen was accurate as labeled. Our goal was to identify the best sunscreens that catered to the unique needs of individuals with medium to darker skin tones.
-
Selection of products
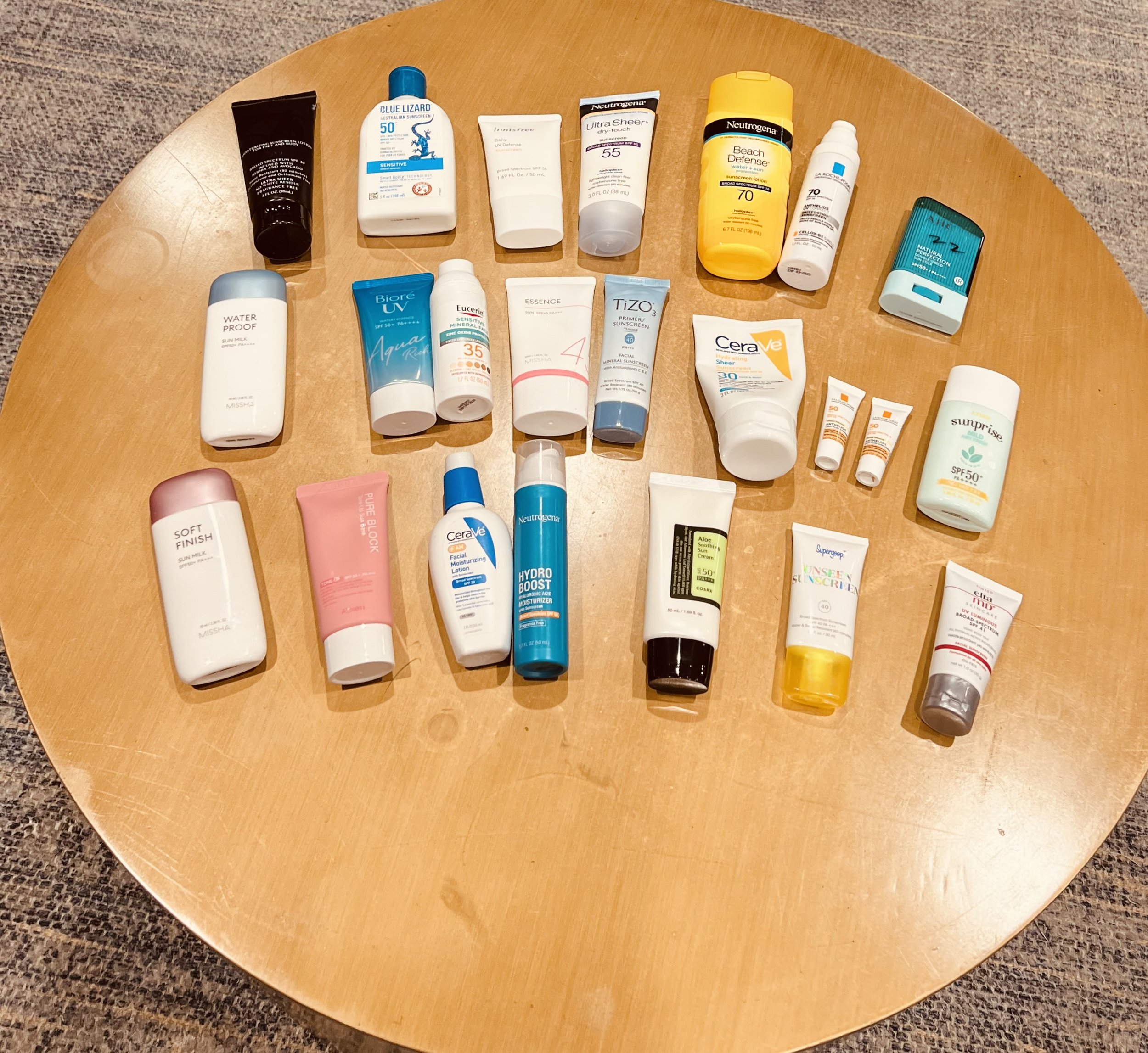
22 of the most popular sunscreens were identified based on a combination of keyword queries for ‘sunscreens’, ‘best sunscreens’, ‘sunscreen for darker skin tones’, ‘Korean sunscreens’, ‘tinted sunscreens’, on Amazon as well as products identified from market research for sunscreens that fit diverse skin tones.
We selected the top 10 most common products encountered during the searches (excluded sponsored products) combined with 12 additional products identified through consumer market research on popular skincare websites.
Testing of products
To preface, this study is one component of a larger testing scheme, where we organized a panel of 6 testers with a wide range of skin tones try a variety of different sunscreens, ranging from chemical, mineral, combination sunscreens, Korean sunscreens, etc.
For the current piece, we focused exclusively on the experiences of our testers with more pigmented skin tones. A panel of 4 testers (Boston-based dermatology residents) with varying skin tones (medium x 1, medium brown x 1, medium dark brown, dark brown) participated in an in-person product testing session. Data analysis was performed using only their recorded metrics.
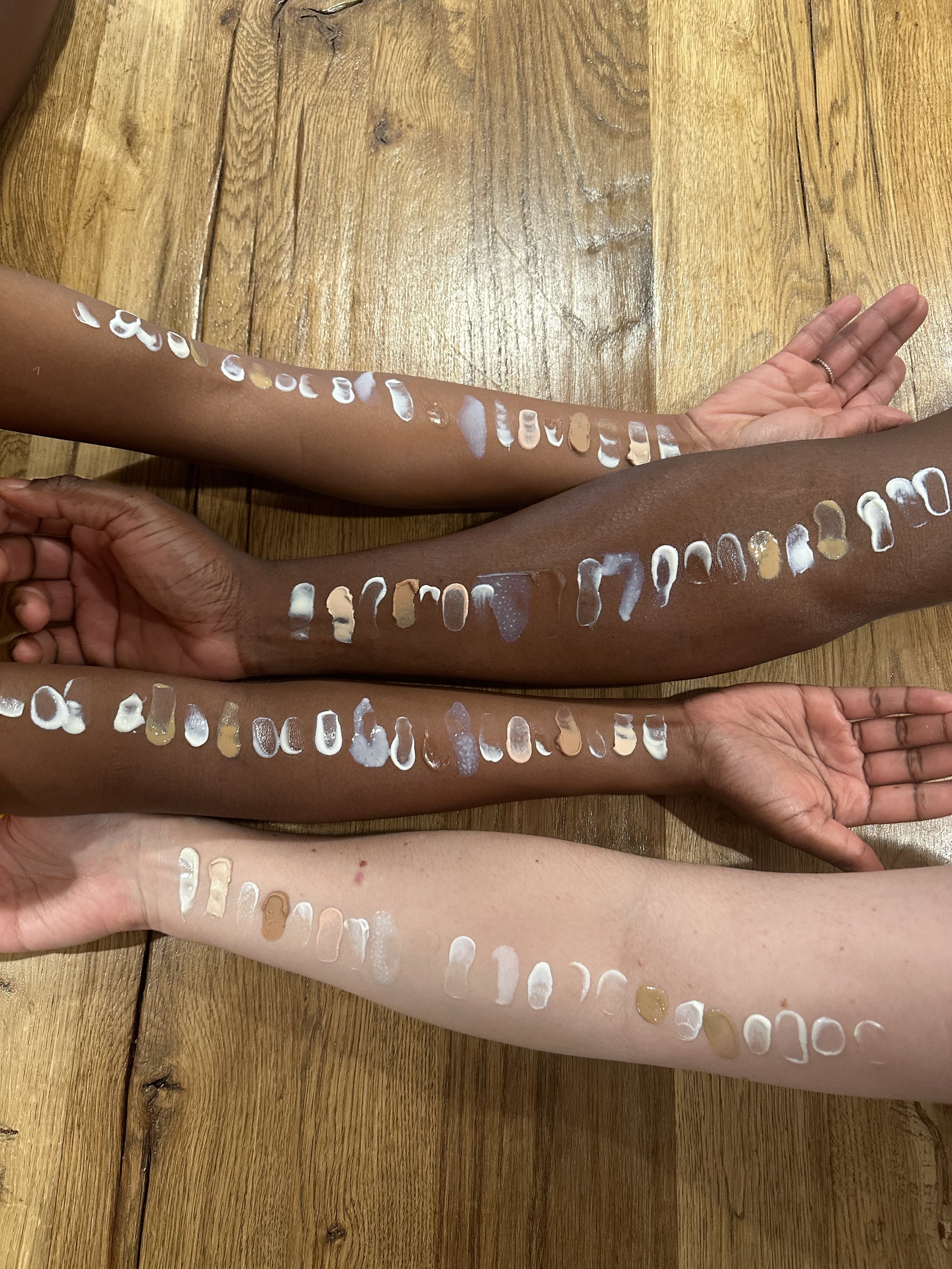
We performed blinded product testing. The brand names of each product were concealed from the testers by allocating a portion of each product to a separate plastic container labeled only with a number. The testers were instructed to apply the different sunscreens over the areas of their forearm with the thinnest skin and to assess pre-defined qualities of each sunscreen. Hypoallergenic wipes were used to remove product in between testing.
The testers focused closely on various factors such as texture, feel, appearance, presence of white cast, greasiness, and scent. Importantly, testers paid close attention to the ease of application, such as how easily the sunscreen was able to be smeared and spread over the skin in an even manner. Select products were also used on the face to assess for compatibility with makeup.
With a commitment to inclusivity, our panel consisted of individuals representing diverse backgrounds and skin characteristics. This approach allowed us to gather insights relevant to the specific needs of those with a wide range of skin tones and body hair textures. By employing these rigorous testing methods and involving a diverse group of testers, we aimed to provide an objective evaluation of each sunscreen's performance. The resulting information will serve as a valuable resource for individuals seeking reliable recommendations tailored to their unique skin requirements.
-
We are a group of dermatology residents and attending physicians based in Boston, MA. Our team of Ivy League-trained dermatologists is demystifying the cosmeceutical industry by offering unbiased, scientifically supported reviews of skincare products. We are extremely passionate about skincare and making it accessible to all through education. We value integrity, practicality, and inclusivity. No sponsorships were received for the products prior to testing; we feel strongly about providing un-biased reviews. After blogs are published, following the links in this blog post may result in commission.
An overview of our core team:
Dr. David Li is a recent graduate from the Harvard Combined Dermatology Residency Program. He is now in private practice as a procedural dermatologist in Downtown Boston where he offers skin cancer screenings, skin cancer surgeries, and laser and cosmetic rejuvenation. He has published more than 25 peer-reviewed research articles, is active as an advisor for multiple early-stage companies, and is an angel investor in the healthcare technology space. In his free time, he enjoys running to stay fit, cooking, and playing with his Australian shepherd, Laika.
Dr. Jacqueline Stevens is currently a resident in the Harvard Combined Dermatology Program. She completed her undergraduate studies and MD-PhD at the University of Virginia with a PhD in microbiology, immunology, and infectious disease. Jacqueline has interest in cutaneous oncology, melanoma, and dermatologic surgery. She has published work on the basic science of inflammation at skin barriers, dermatologic diseases, and systems used to classify squamous cell skin cancer. In her free time, she enjoys skiing, hanging with her rescue pup, and the outdoors.
Dr. Olivia Davies is a dermatology resident at the Harvard Combined Dermatology Residency Program. Her dermatology interests include inpatient dermatology, complex-medical dermatology and medical education. She enjoys exploring the intersection between medicine and media — with past experiences that include rotating through the ABC News Medical Unit, publishing a graphic perspective in the New England Journal, and serving as a poetry editor for Intima: A Journal of Narrative Medicine. When she’s not learning or working, she can be found making cheese plates for friends, sipping a warm cup of coffee, or solving the newest NYT crossword puzzle.
Dr. Nelson Ugwu is a dermatology resident at the Harvard Combined Dermatology Residency Program. His clinical interests include general dermatology, skin of color and skin cancer prevention. Nelson has discovered mutations that cause skin diseases, as well as new treatments for skin conditions. In his free time, Nelson enjoys weightlifting, playing soccer and trying new recipes.
Dr. Arash Mostaghimi is an associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, the director of the inpatient dermatology consult service, and co-director of the Complex Medical Dermatology Fellowship at Brigham & Women’s Hospital. He is also the principal investigator of the Mostaghimi Lab, where he leads a diverse group of physicians and researchers to study alopecia areata, an autoimmune hair loss condition which afflicts his daughter. In addition to his research, he is an advisor to multiple companies and is an associate editor of JAMA Dermatology.
Additional contributors and testers for this study:
Dr. Victoria Humphrey is a dermatology resident at the Harvard Combined Dermatology Residency Program.
Dr. Anusha Kumar is a dermatology resident at the Harvard Combined Dermatology Residency Program.
-
Patients are often concerned about the efficacy and suitability of sunscreen for darker skin tones. Many individuals with darker and deeper skin tones struggle with white cast (glossary), irritation from sweat, and uneven blending with makeup when using sunscreen. This is partially due to the lack of reliable information and product recommendations specifically tailored to their needs. As a result, users are often concerned about the efficacy and suitability of sunscreen for darker skin tones.
We aim to address these concerns by providing comprehensive information and recommendations on sunscreen for medium to darker skin tones. This article will guide you to make informed decisions about sunscreen to ensure optimal skin protection and address your unique skincare concerns.
-
When selecting a sunscreen, many individuals with medium to darker skin tones desire a product that does not leave a white cast. Two common key ingredients in mineral sunscreen which leave a white cast and visible residue on the skin are:
Zinc oxide
Titanium dioxide
Sunscreens formulated with micronized or nano zinc oxide or nano titanium dioxide, which consist of smaller particles, are less likely to leave behind a noticeable white cast. Sunscreens that offer protection against visible light, in addition to UVA and UVB rays, are particularly beneficial for those with darker skin tones as they can protect against skin discoloration.
Another factor to consider (not required for all cases) is tint. In patients with more pigmented skin, the light from the visible light spectrum can lead to hyperpigmentation and discoloration, especially after injuries to the skin or scars. For this reason, we recommend tinted sunscreens for certain cases. Tinted sunscreens contain iron oxide which protects against visible light. Tinted sunscreens usually have a light brown finish to them, and in patients with darker skin tones, this may not be very noticeable.
Sunscreen texture and consistency are other important properties to consider. Some sunscreens may feel heavy or greasy on the skin, making them less desirable for daily wear.
Look for sunscreens that are:
Lightweight
Non-greasy
Quick to absorb
Sweat-proof or water-resistant
Broad spectrum SPF protection
One other factor to consider is the sun protection factor (SPF). The American Academy of Dermatology recommends using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. This provides adequate protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
It is also important to remember to reapply sunscreen every two hours or after swimming or sweating to ensure continuous and effective protection.
-
Misconception: Contrary to popular belief, individuals with medium to darker skin tones are not immune to the damaging effects of the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Melanin's Role: While natural melanin provides some inherent protection, it does not eliminate the risk of sunburn, skin damage, skin cancers, and skin discoloration.
Importance of Sunscreen: Sunscreen plays a crucial role in protecting all skin types, including patients with medium to darker skin tones, from the effects of UV radiation and visible light.
Consistent Usage: By using sunscreen consistently and appropriately, individuals with darker skin tones can maintain healthier and radiant skin while minimizing the risk of sun-induced skin issues.
-
Sun damage is a significant contributor to premature skin aging.
Prolonged and unprotected exposure to the sun's UV radiation can lead to the breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers in the skin (glossary), resulting in the formation of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
Individuals with medium to darker skin tones may experience different manifestations of sun damage, including uneven skin tone, hyperpigmentation, and dark spots. By diligently using sunscreen, particularly those formulated for darker skin tones, individuals can minimize the long-term effects of sun damage and maintain a more youthful appearance and even complexion.
-
Types of sunscreen: Sunscreens can be separated into mineral and chemical sunscreens.
Mineral sunscreens contain active ingredients such as titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, which create a physical barrier on the skin to reflect and scatter UV rays. They are often preferred for their gentler nature and less likelihood of causing irritation. As previously mentioned, mineral sunscreens are more likely to leave a white cast. Tinted sunscreens are a type of mineral sunscreen which contain iron oxide or pigmentary titanium oxide. These ingredients allow a broad range of skin tone matching and also provide protection against visible light, which can lead to skin discoloration in individuals with darker skin tones.
Chemical sunscreens, on the other hand, work by absorbing UV rays and converting them into heat. They typically contain ingredients like avobenzone, octinoxate, or oxybenzone. Chemical sunscreens are less likely to leave a white cast but may cause some skin irritation especially in patients with sensitive skin.
Combination sunscreens may utilize both mineral and chemical filters to provide broad-spectrum protection. These hybrid formulas aim to combine the benefits of both types while minimizing potential drawbacks.
-
SPF (Sun Protection Factor) is a measure of a sunscreen's ability to protect the skin from UV rays, which are primarily responsible for sunburns. It indicates the degree of protection provided compared to unprotected skin.
Higher SPF values indicate more significant protection, although it's important to note that no sunscreen can provide 100% protection. SPF should be considered in conjunction with other factors such as application frequency and adequate coverage.
-
What are the best sunscreens for medium to dark skin tones?
The best sunscreens for dark skin tones are those that offer broad-spectrum SPF protection, do not leave a white cast, and are hydrating. Ultimately it comes down to user preference, but see our top picks for a list of what we think are the best sunscreens for medium to darker skin tones.
What is the hype I am hearing about tinted sunscreens?
Tinted sunscreens can provide protection against visible light, which can lead to hyperpigmentation. Visible light is a large part of skin darkening in patients of darker skin tones, and tinted sunscreens contain iron oxide which protects against this process. For this reason, we often recommend patients with recent injuries to the skin (e.g. scars, cuts) to apply a tinted sunscreen to prevent hyperpigmentation.
What is the importance of SPF in sunscreen?
SPF, or Sun Protection Factor, measures a sunscreen's ability to protect the skin from UVB rays, which cause sunburn and contribute to skin cancer. Dermatologists recommend using a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for adequate protection.
What should I look for in a sunscreen for acne-prone skin?
For acne-prone skin, look for a non-comedogenic sunscreen that won't clog pores. Oil-free and lightweight formulas can also help prevent breakouts. Some sunscreens even contain ingredients like hyaluronic acid to provide hydration without causing acne.
Why is it important to wear sunscreen every day?
Daily sunscreen use is crucial for protecting your skin from harmful UV rays, which can cause premature aging, hyperpigmentation, and skin cancer. This is true even for darker skin tones, which can still be damaged by UV exposure.
What is the role of moisturizer in a sunscreen?
Many sunscreens include moisturizing ingredients to hydrate the skin while providing sun protection. This can be beneficial for maintaining skin health and preventing dryness. Look for sunscreens with ingredients like hyaluronic acid for added hydration.
What is the difference between sunscreen lotion and sunscreen oil?
Sunscreen lotions are typically thicker and provide more moisture, making them suitable for dry skin. Sunscreen oils are usually lighter and absorb quickly, which can be preferable for oily or combination skin types. However, note that we did not test any sunscreen oils.
What are some sunscreens that do not leave behind a white cast?
Our favorites are the UNSEEN SUNSCREEN Supergoop SPF 40 and the La Roche Posay Anthelios UV Correct Sunscreen Moisturizer SPF 70.
What is the difference between mineral and chemical sunscreen?
Mineral sunscreens use active mineral ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide to reflect UV rays away from the skin. Chemical sunscreens, on the other hand, absorb UV rays and convert them into heat. Both types can be effective, but mineral sunscreens are often recommended for sensitive skin.
-
Our experiment underscores the importance of using sunscreen for medium to darker skin tones and provides valuable insights into selecting the right product.
We tested a variety of sunscreens:
Mineral Sunscreen (including tinted products)
Chemical Sunscreen
Combination Sunscreens
We also tested sunscreens with varying SPF levels, from SPF 30 to SPF 50.
We found that 4 properties were most important:
SPF protection - high (spf 30-50 at least)
Texture/consistency - non-greasy
Appearance - does not leave a white cast
Ease of application - easy to apply and blend into skin
When selecting a sunscreen, it's also important to consider the individual's skin type:
Oily Skin: Prefer a lightweight, non-greasy sunscreen
Dry Skin: Benefit from a hydrating sunscreen with a built-in moisturizer
Sensitive Skin: May prefer a mineral sunscreen with few fragrances
-
American Academy of Dermatology. (n.d.). Skin cancer in people of color. Retrieved March 29, 2022, from https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-c
Torres AE, Awosika O, Maghfour J, Taylor S, Lim HW. Practical guide to tinted sunscreens. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022 Sep;87(3):656-657. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.12.040. Epub 2021 Dec 30. PMID: 34973975.
-
La Roche Posay Anthelios UV Correct Sunscreen Moisturizer SPF 70
EltaMD UV Luminous SPF 41 Mineral
Neutrogena Beach Defense SPF70
TIZO Primer Sunscreen SPF40
Black Girl Sunscreen SPF 30
A'PIEU Pure Block Tone Up Sunscreen SPF 50
CeraVe SPF30 Facial Moisturizing Lotion
MISSHA All Around Safe Block Waterproof Sun Milk SPF50
UNSEEN SUNSCREEN Supergoop SPF 40
Neutrogena Ultra Sheer Dry Touch SPF 55
MISSHA Soft Finish SPF50
Blue Lizard Mineral Sunscreen SPF50
Neutrogena Hydro Boost Hyaluronic Acid Facial Moisturizer with Broad Spectrum SPF 50
Bioré Japan Aqua Rich Watery Essence Sunblock Sunscreen Blue SPF 50
Eucerin Sun Tinted Mineral Face Sunscreen Lotion SPF 35
CosRx Aloe Soothing Sun Cream SPF50
Laroche-Posay Anthelios Tinted SPF 50
innisfree Daily UV Defense Sunscreen Broad Spectrum SPF SPF 36
CeraVe Hydrating Sheer Sunscreen SPF 30 for Face and Body, Mineral Sunscreen & Chemical Sunscreen
ETUDE HOUSE Sunprise Mild Airy Finish Sun Milk SPF50
MISSHA - All-Around Safe Block Essence Sun SPF45
AHC Natural Perfection Fresh Sun Stick 22g SPF 50